Training Tiny LLMs to Play Connections Better than Frontier Models



Reasoning is the talk of the town - if the 'town' in question is AI Twitter - and has been since OpenAI's announcement of O1 in late 2024. A number of similar 'reasoning' models have followed, some open, like Qwen's QWQ, and some propietary, like DeepSeek's R1 and Google's Gemini Flash Thinking; however, as is often the case with LLM releases these days, little research has been published from each of these groups on how exactly these reasoning models are trained. What we do know is that these models are expensive and difficult to train, requiring the kinds of resources that are rare outside of large labs; distributed PPO-based RLHF is already prohibitively expensive and complex, owing to requiring a large number of distinct operations and model sync points during training, so you can imagine the difficulty in scaling that to the amount of data and compute required to train a reasoning model.

Whenever a new technical report is released for an open LLM, I like to give it a skim to see if there are any novel post-training techniques, as that's what I've been working on lately. When these techniques are used in large-scale models available to the public, it's more convincing to me than when it's demonstrated in a standalone paper or a small-scale model. This post is a roundup of some of the techniques I've seen in recent reports, and a brief overview of how they work.
Unfortunately, none of these model reports contain ablation metrics for the techniques reviewed; at their scale, it might have been prohibitively expensive to do so, but this does leave the question open as to how effective these techniques are in isolation[^1]. I'll also be skipping details not related to post-training techniques, so this won't be a full paper review; I'd suggest checking Sebastian Raschka's blog for more in-depth reviews of papers in that vein.

I've been experimenting with different techniques for fine-tuning LLMs to improve on code generation tasks, as I find it an interesting domain for testing alignment techniques for a few reasons:
However, the piece that's still under heavy development is the post-training or alignment piece. While reward models, and RLCEF models exist, they're expensive to train and often unstable; so I've been exploring the possibility of using preference models like DPO instead.

TL;DR: I've created a synthetic dataset for training LLMs to use tools, and am training a model using DPO to improve accuracy. The dataset is available here, and I'll be releasing trained models soon.
When ChatGPT emerged, its initial utility as a search engine replacement and knowledge engine. However, over time, it became clear that it, and models of its class, possessed far more interesting skills: some degree of reasoning ability, and even the ability to perform tasks by outputting structured text (i.e. tool calls). This sparked excitement about its potential as an "agent" capable of interacting with the world. Demos followed, from buying things on the internet to more general tasks like making $100k(!). For a brief period after ChatGPT's launch, it seemed that all we needed to do was find the right agent framework, the correct system prompt, and boom, we'd have AGI.
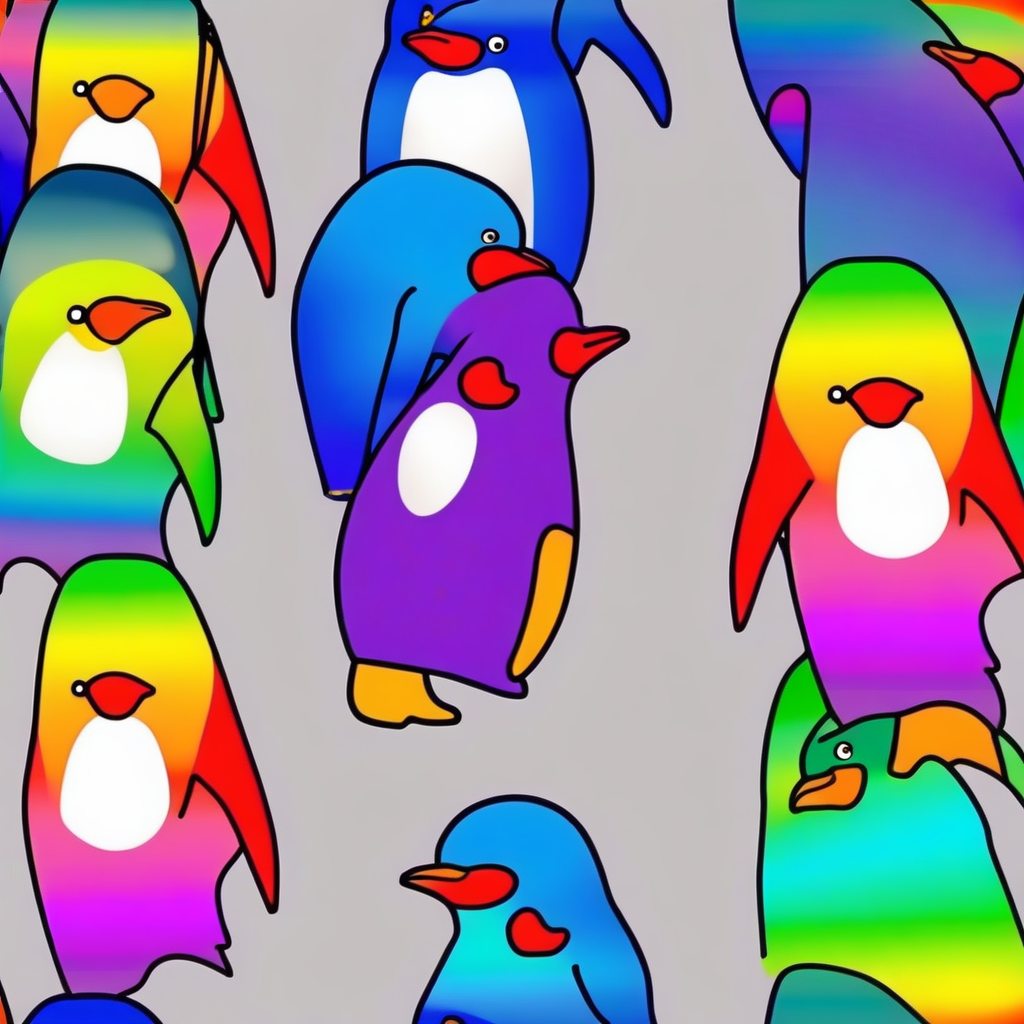
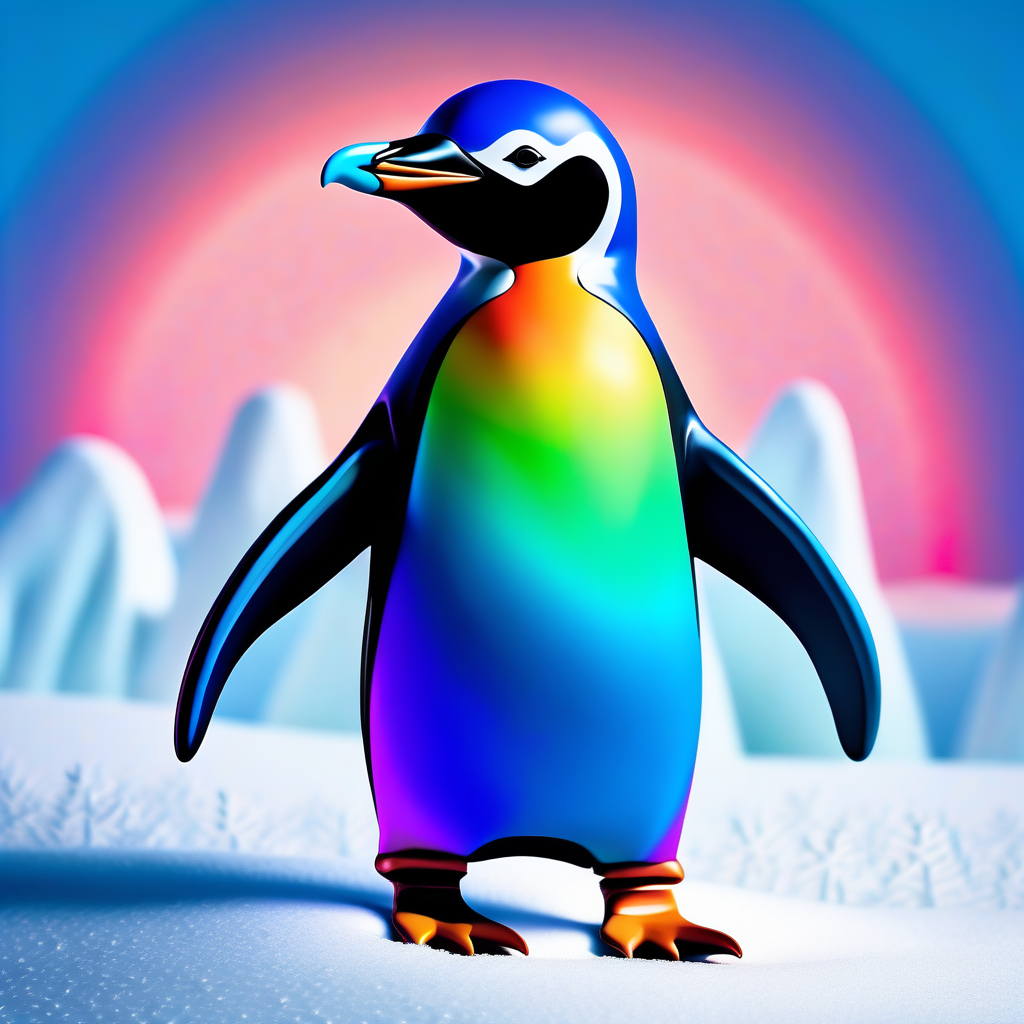


Left: Drawbench prompt "A rainbow penguin in a tuxedo". Right: SDXL output with SuperPrompt applied to the same input prompt.
TL;DR: I've trained a 77M T5 model to expand prompts, and it meets or exceeds existing 1B+ parameter LLMs in quality and prompt alignment.
When DALL-E 3 was released, I was a) really impressed, and b) struck by how obviously good an idea the prompt augmentation it uses was. To that end, I've spent some time over the last few months playing around with some various approaches to emulate that functionality.

For the last two years, the improvement in fidelity and control in diffusion models has been incredible; generation results are often indistinguishable from real images, and a huge ecoystem of tools has emerged to offer various forms of control over the generation process. However, for a lot of real-world workflows, you quickly run up against limitations that make things hard for less technical users.
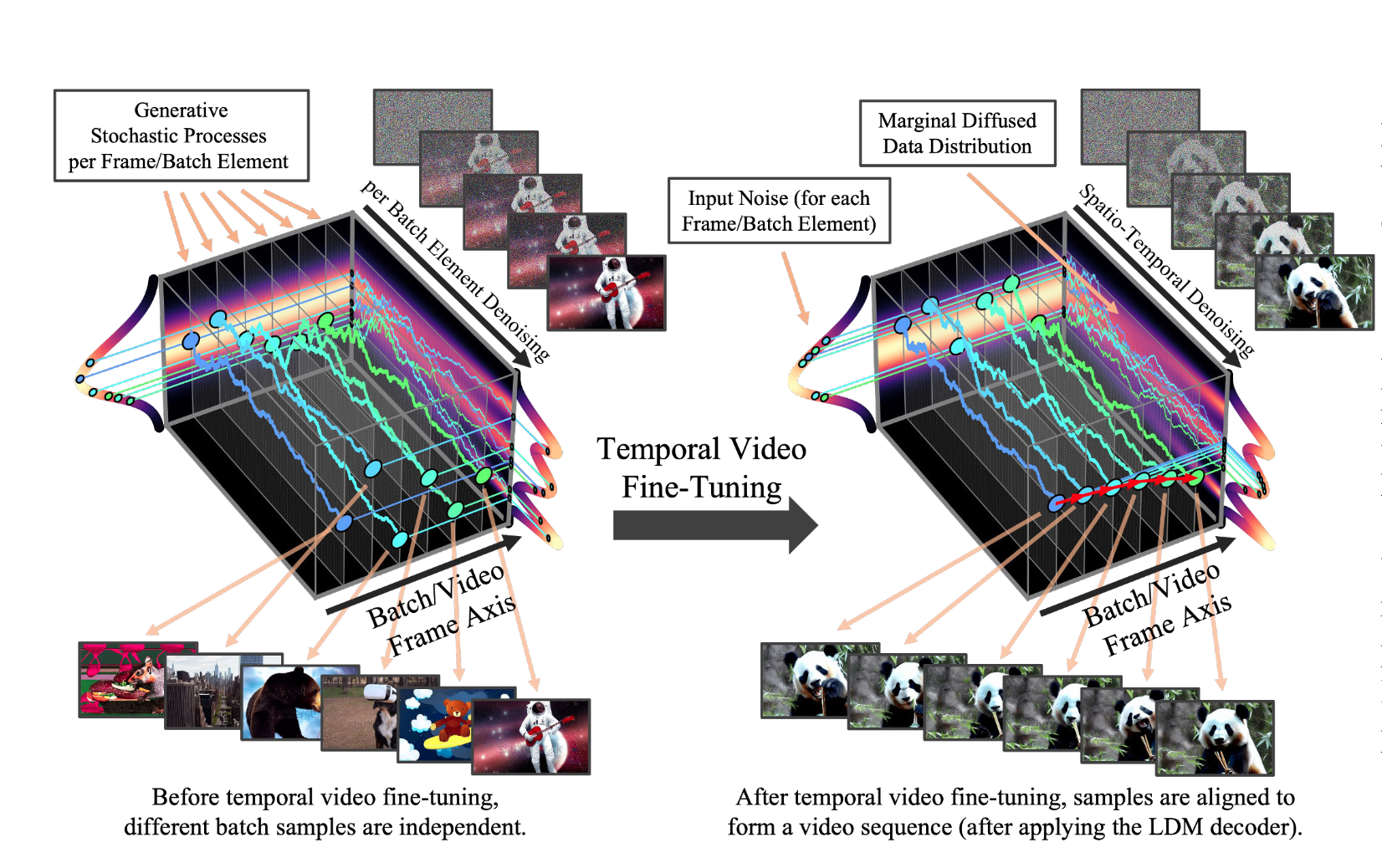
Text-to-video diffusion models have started to mature massively in the last few months; starting roughly with Gen-1 and Pika, and increasing in popularity in open-source with AnimateDiff and now Stable Video Diffusion.
In most video diffusion models, including Stable Video Diffusion this is because the diffusion process is being applied across the entire batch; you can think of SVD inference as denoising a batch of latents concurrently, as done in text-to-image diffusion models; though in this case, the U-net is attending to all latents at once (technically, through separate temporal and spatial layers). As you can imagine, this is very compute-intensive; this also means the model has only seen videos up to a few seconds long (though at different framerates), due to training costs increasing with batch size. If you try to generate longer videos, i.e. past 14 frames with SVD and 25 with SVD-XT, the coherence and motion suffer.